Wordpress
Make WordPress work for You!
472 million websites use WordPress, which is 43.3% of all the websites on the internet.
We manage many websites that are built on WordPress.
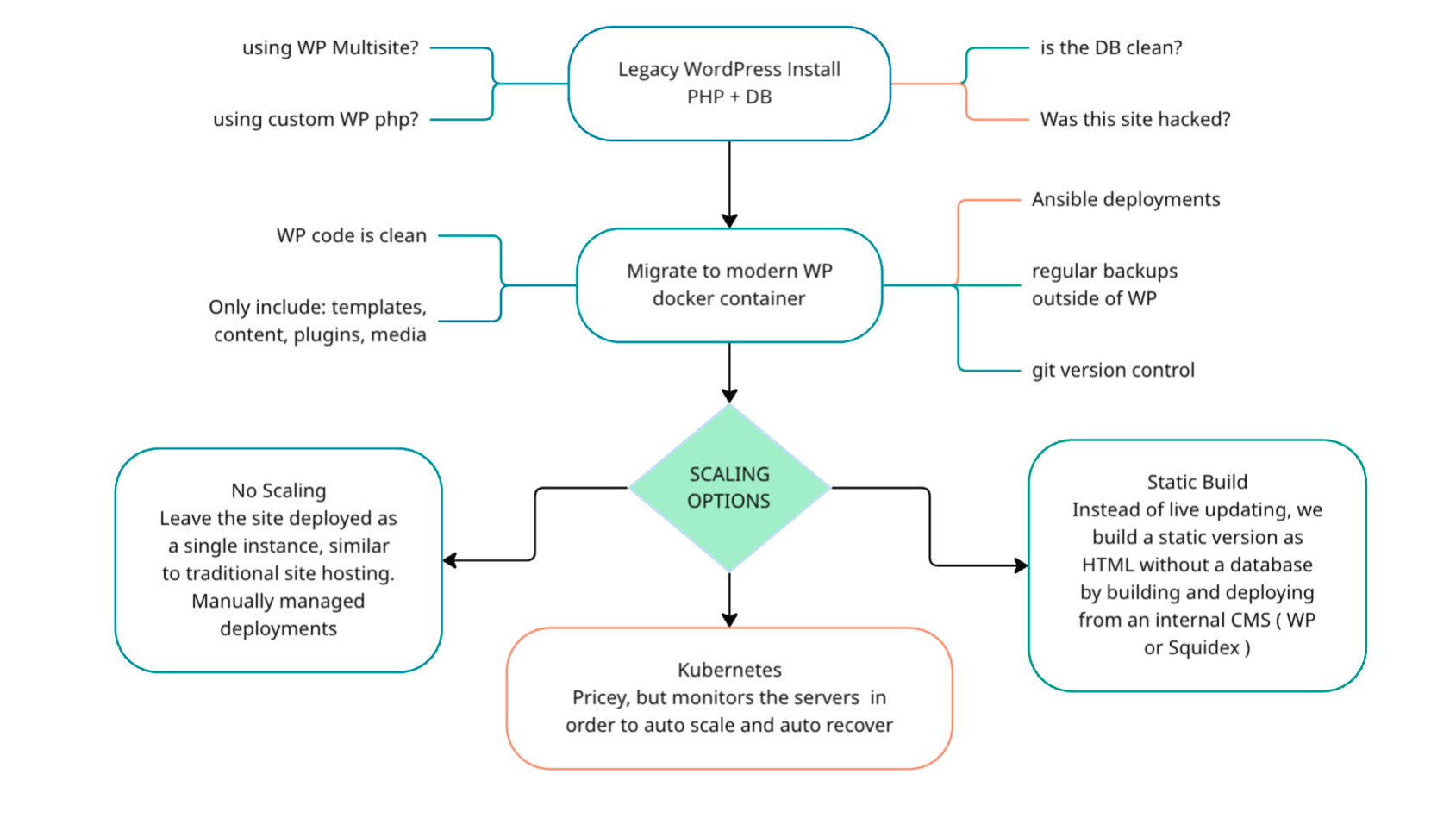
First we need to migrate it from a legacy installation to a version controlled and container based system so that developers can work with it properly.
Once we’ve modernized the site itself, we can choose one of 3 options to handle all the scaling needs, if required.
Legacy WordPress
It doesn’t matter if your particular version of WordPress was had the php modified, was hacked 6 years ago or is using a multisite configuration with an unmanagable database, we’ve seen it all. We can help fix things right up… just not in the same way that things worked before is all.
Migrate to a modern Docker based WordPress
First, let’s migrate the data off that old server and move it over to a modern “container”. This allows us to rely of trusted versions of WordPress itself at all times. From here, we only need to add in our content and any extras.
This also allows us to version control the site properly, which developers appreciate.
Scaling Options
Now that the site is using containers, we have a few options with how to scale.
1 - No Scaling
It can often be best for small to medium sites to not worry about scaling at first, at least until it becomes an issue. Moving to a container is already helping to keep the server needs down, allowing for some extra overhead.
2 - Kubernetes
Kubernetes can be a bit costly, but for a good reason; Its able to closely monitor the performance of the website in order to both scale the server or attempt to auto recover in the case of an error.
3 - Static Site ( recommended )
Usually a wordpress site doesn’t need to be “live” or “Dynamic”, which means it might be better to build a “static” version in plain HTML, and update that any time there is a change. This lets us use modern tools and JavaScript frameworks as well as not needing a database or a dedicated server to host content since all the content is included.
Next Steps
Let’s discuss the differences of each, which will be interesting to anyone who is running their own WordPress website. The options here are, mostly, about
how we work with the content itself when using WordPress.